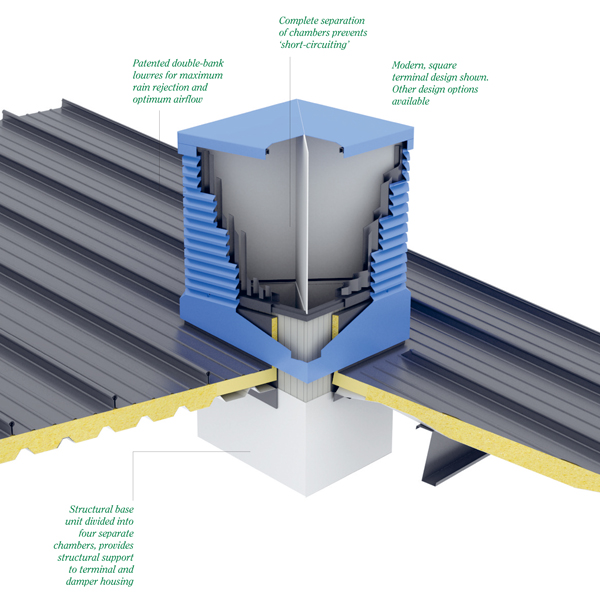
Passivent Airscoop® is a range of roof mounted natural ventilation terminals which provide top-down or displacement ventilation to large buildings and deep plan spaces.
They are designed to ‘capture’ prevailing wind and direct it via four separate chambers within the terminal to the space beneath. Research shows that air is constantly entering one or more of the chambers or exhausting via one or more of the chambers depending on prevailing wind speed and direction. See ‘Features and benefits’ below for further details about our 15 Year No Leak Guarantee and also information about modelling the Airscoop within the IES Virtual Environment.
Features and benefits
- Environmentally friendly and energy saving natural ventilation, no power is required to move the air.
- Optimised segmented design delivers maximum airflow capacity with minimal pressure drop through the system.
- Complete separation of chambers in the entire system prevents “short circuiting”.
- Circular and square terminals available in a range of designs.
- Patented double bank louvres provide Class A rain rejection (BS EN 13030:2001) so that your building can be fully ventilated regardless of weather conditions.
- Resistant to continuous wind loads at 51 m/s (BRE tested).
- 4mm insect screen to prevent ingress of insects and other debris.
- Passivent Airscoops® are covered by our 15 Year No Leak Guarantee. No annual servicing is required for this guarantee as there are no mechanical/electrical items such as actuators, within the terminal to maintain, therefore no external/roof access is required. For further information on the guarantee see…
- The Airscoops® is available for modelling within the IES Virtual Environment providing a fast, streamlined and easy-to-use method of simulating the effect of this roof terminal within VE models. A dedicated VE navigator has been created to guide users through a stepped process from importing the products into your model, configuring your operation, preparing and applying to rooms, thermal simulation and compliance analysis. Click here for more information.